Electronic barcodes were created to reduce human input error and accelerate cataloging of items.
1D, or one-dimensional barcodes, are strips of black lines with white spaces found on packaging which are read by a scanning device, either handheld or flatbed reader.

1D barcodes work well when scanning single items at a time, like when checking out groceries or homewares at your favorite department store.
1D barcodes are not very efficient in the typical laboratory where large volumes of patient samples need to be processed quickly.
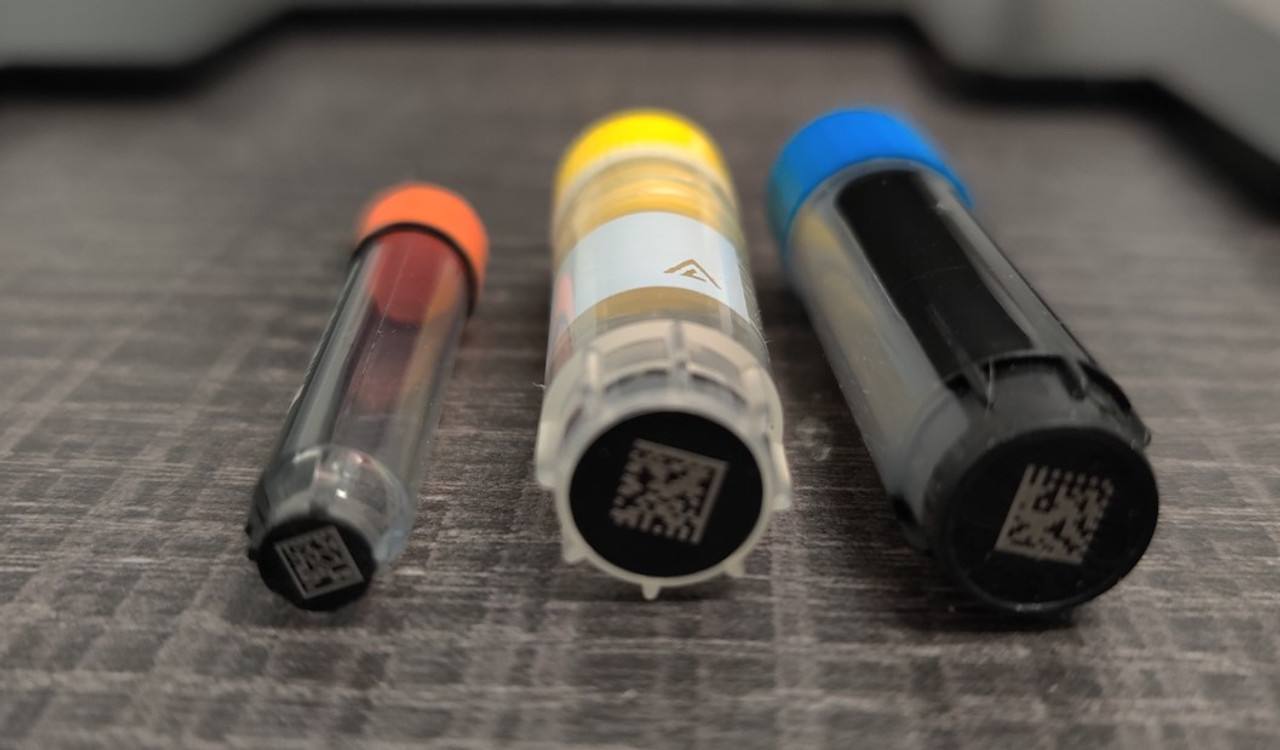
2D barcodes are encoded symbols, similar to a QR code, and not black and white lines.

A 2D barcode is located on the bottom of a cryogenic tube that is stored together with other tubes in a single rack.
Using a flatbed scanner an entire rack of 2D barcoded tubes can be read in seconds.
This is because the bottom of the rack is designed with gaps allowing the 2D barcode to be visible.

What to look for in a 2D barcoded tube
Like all cryogenic vials, 2D barcoded tubes need to be made from durable polypropylene that can withstand temperatures as low as -196C, which is the gas phase of liquid nitrogen.
To ensure sample integrity and safety, 2D barcoded tubes must be sealable with air and liquid-tight caps.
Most commonly, a silicone O-ring is placed around the tube neck which compresses when tightened to form a seal.

If human samples are being stored, the 2D barcode needs to be certified STERILE, but for all other applications RNase and DNase free generally is sufficient.
To ensure sample security the 2D barcode must be part of the storage tube and not fused together from a separate piece of plastic.

The barcode itself must be rigorously tested to guarantee no reading errors, even after years of handling.
2D barcoded tubes are designed for lab automation
The 2D barcode allows for rapid scanning and identification of samples, while two other features make these cryovials ideal for robotic systems:
2D barcoded tube caps are designed with grooves that fit a shaped driver which is rotated to open and close the tube.

To prevent the tube from spinning in place during the capping or decapping, tube bottoms have protruding “feet” to lock them into tube racks.
Combining these special design features allows a laboratory to program a robot to:
1) Scan/read and identify a sample 2) Uncap the sample 3) Load the sample onto a liquid handler 4) Aspirate samples from the 2D barcoded tube 5) Return the tube to its rack. And 6) Recap the tube
Do 2D barcoded cryovials require any special storing?
2D barcoded tubes can be stored in any cryogenic box that is appropriate for the temperature the samples require.
Where automation is not done, a simple cardboard box will suffice for -80C or -196C storage units.
To take full advantage of the 2D barcode system, it is necessary to purchase boxes or racks with openings below so the scanner can read the full rack of tubes.
High quality polycarbonate racks from AltemisLab stand up to harsh storage conditions and brighten up any lab with a splash of sunshine yellow.

AltemisLab tube racks have their own embedded barcode so when scanning a rack of 2D barcoded tubes, not only is each tube identified independently, but they are associated with the specific storage rack.

2D barcode tube racks from AltemisLab are available with an SBS footprint of 48 or 96 tubes, and large formatted of 81 or 100 places, to complement tube volumes from 0.5mL to 5mL.
2D barcoded tubes are perfect for any lab that demands a high level of sample security and confidence.
Stellar Scientific and AltemisLab have 2D barcoded tubes and lab automation tools to begin taking control of your samples through full automation.