Brief Overview of use and Applications
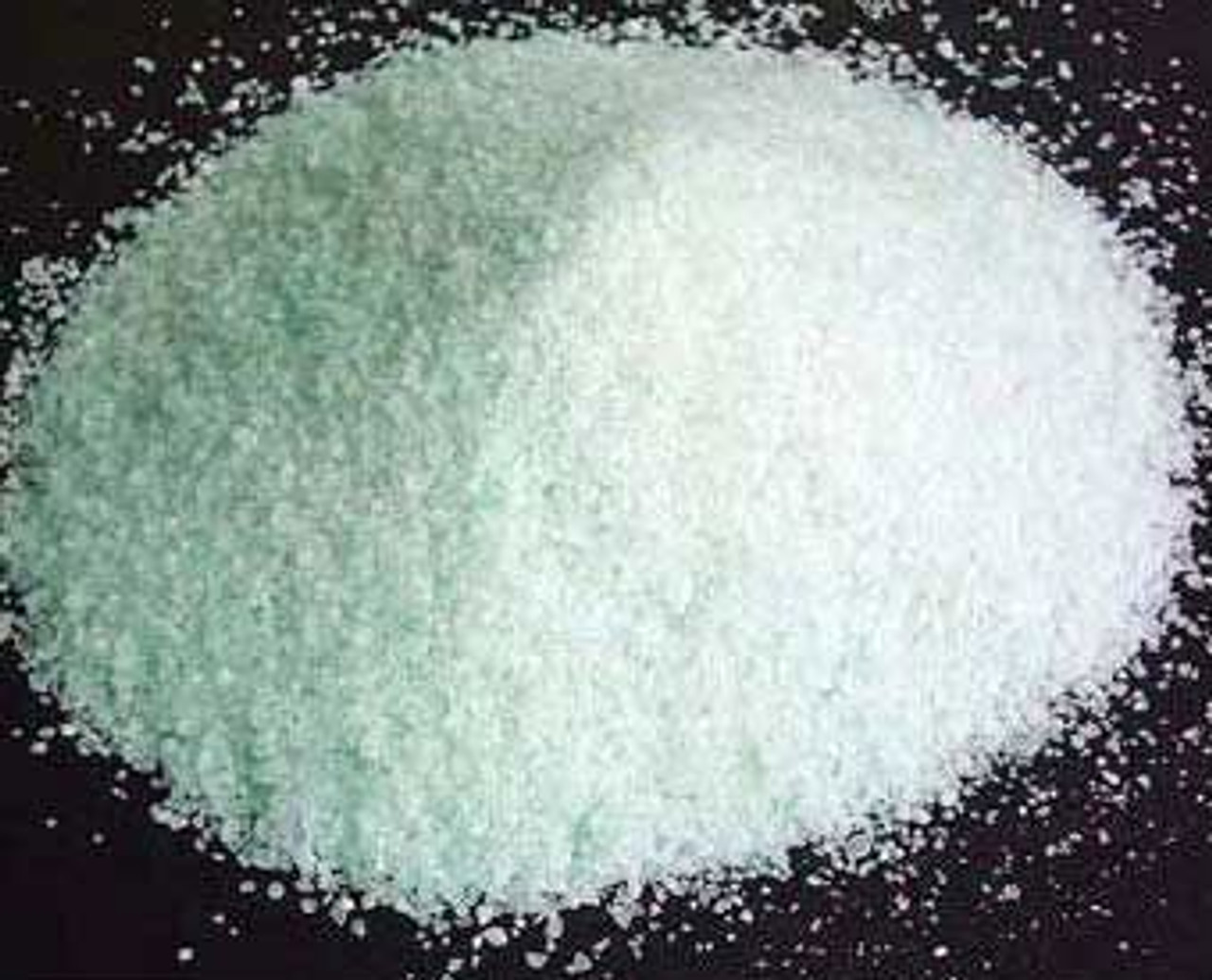
Barium Chloride is an inorganic salt that comes as a white crystalline powder. It is probably best known as an additive in fireworks and a purifying agent for brine.
This compound gives a distinctive green color to certain fireworks and paints
Despite this ambiguous reputation, it has many potential applications and is used frequently in industry.
Important Physical Characteristics
Barium Chloride (Formula: BaCl2) is a crystalline powder made from the elements barium and chloride. It’s colorless, odorless, and water soluble up to 38%.
It is highly toxic and alkaline, has a molecular weight of 208.23 g/mol, and a density of 3.86 g/cm3.
It has a melting point of 960°C and boiling point of 1560°C at standard pressure.
Chemical Behavior and Reactivity
This salt is one of the more reactive elements, and useful in chemical industry applications because it interacts with so many substances.
Common Reaction Partners:
- Oxygen
- Sulfate
- Water
- Carbon and sulfur compounds
Popular Applications in Industry
It has a long history of use in the creation of pigments, as a water softener, and in pharmaceuticals.
Because of its reactivity it has very broad applications.
Below is a list of some of other common uses:
- Wastewater treatment
- Brine purification
- Pesticides
- Production of stabilizers, polymers, and other salts
Research Connections using Barium Chloride
This substance is toxic if ingested and capable of causing severe muscle contractions, but does have limited applications in biology and medicine.
Biology Research
In one example, it’s used as a model for muscle injury, but may not produce realistic results.
The study in question demonstrated that Barium induced muscle injury has limitations as a model, but may be used as a simple alternative to other types of chemical injury.
Medical Applications
Barium has been used as a crosslinker in the development of bioabsorbable sutures because it reacts with alginate molecules in solution.
This example study extruded alginate polymer onto a hydrogel with 2% BaCl2 to create functional sutures.
Other Connections
It can be used to induce muscle contractions in both skeletal and smooth muscle, and is given at very low doses to horses when they are impacted.
It is commonly used as a rodenticide, and its prevalence in industry also makes it a chemical of interest for environmental toxicity studies.
Safe use and Handling in the Lab
When working with this Barium salt, always use gloves and dispose or wash contaminated materials afterwards.
Do not attempt to vaporize it in the open, and seek medical attention if ingested.
Because it is an environmental toxin, disposal should be handled with care. Dispose in a designated waste container for removal by a chemical disposal service.
In terms of chemical reactivity, never combine it with Bromine Triflouride or the statin and prostate drug 2-Furoic Acid.
Never dispose of chemicals in the sink. It poses an environmental hazard to humans and other life forms.
Browse our Full Catalog of Laboratory Chemicals
Stellar Scientific is a small, family owned business that offers a wide array of products to rival any. We pride ourselves in making sure that customers find what they are looking for.
We carry top-quality bulk chemicals for application in any field, and we try our best to cater to the consumer.
See the product page for our ACS grade Barium Chloride, available in a five pound container.
If you have a question about a product or want to settle an issue, we’re available 8:30AM to 6:30PM Monday through Thursday (EST), and 8:30AM to 4PM Fridays. Visit our contact us page for more information.
Footnotes:
_____________________________
- de la Harpe KM, Marimuthu T, Kondiah PPD, Kumar P, Ubanako P, Choonara YE. Synthesis of a novel monofilament bioabsorbable suture for biomedical applications. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2022 Oct;110(10):2189-2210. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.35069. Epub 2022 Apr 4. PMID: 35373911; PMCID: PMC9546231.
- Hardy, David, et al. “Comparative study of injury models for studying muscle regeneration in mice.” PLOS ONE, vol. 11, no. 1, 25 Jan. 2016, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0147198.
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. "PubChem Compound Summary for CID 25204, Barium chloride" PubChem, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0147198. Accessed 29 May, 2024.
- NOAA Office of Response and Restoration, US GOV. “Search Chemicals.” NOAA, cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/19846. Accessed 6 June 2024.
- Ropp, R.C. “Group 17 (H, F, cl, br, I) alkaline earth compounds.” Encyclopedia of the Alkaline Earth Compounds, 2013, pp. 25–104, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0147198.